Photography is the art of capturing light. To control how your image looks, you need to understand three fundamental settings on your camera: ISO, Shutter Speed, and Aperture. Together, they form what is called the Exposure Triangle.
📷 The Exposure Triangle
The exposure triangle is a visual model that helps photographers balance three key elements to achieve a well-exposed photograph.
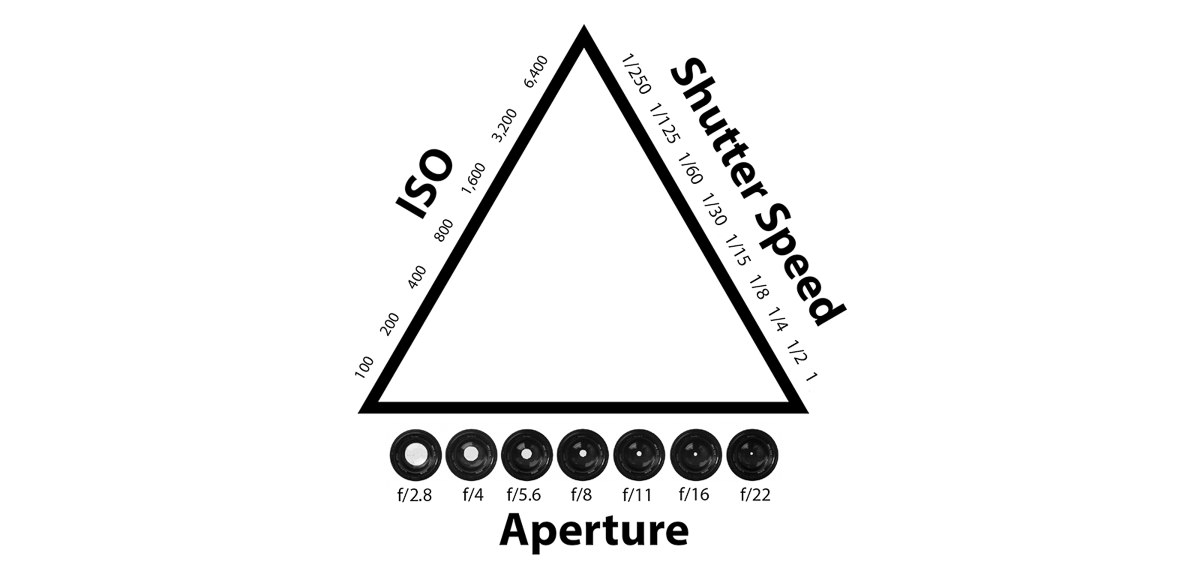
1. ISO 📈
ISO refers to your camera sensor’s sensitivity to light.
- Low ISO (e.g., 100) = Less sensitivity = Cleaner images with less noise.
- High ISO (e.g., 3200 or more) = More sensitivity = Brighter images in low light but with more grain/noise.
Tip: Use the lowest ISO possible for the cleanest result unless light is limited.
2. Shutter Speed ⏱️
Shutter speed is how long the camera shutter stays open.
- Fast shutter (1/1000 sec) freezes motion (great for sports).
- Slow shutter (1/10 sec or slower) captures motion blur or low light (great for night shots or light trails).
Tip: Always match shutter speed to your subject’s motion. Use a tripod for long exposures.
3. Aperture 🔘 (f-stop)
Aperture controls how wide the lens opens to let in light.
- Wide aperture (f/1.8) = More light + shallow depth of field (blurry background).
- Narrow aperture (f/16) = Less light + more in focus.
Tip: Portraits benefit from wide apertures. Landscapes benefit from narrow ones.
🎯 Balancing the Triangle
Changing one setting affects the others. For example, if you increase the shutter speed (letting in less light), you may need to raise the ISO or open the aperture to compensate.
Understanding this relationship gives you creative control over:
- Exposure
- Motion blur
- Background blur (bokeh)
- Image quality
Final Thoughts
Mastering the exposure triangle is essential to move from auto to manual mode. Start experimenting with each setting individually to see how they affect your shots. Over time, you’ll begin to make decisions instinctively.
Happy shooting! 📸


Comments